Multi-LiDAR Roadside Intelligent Perception Method Fusing High-Definition Map
-
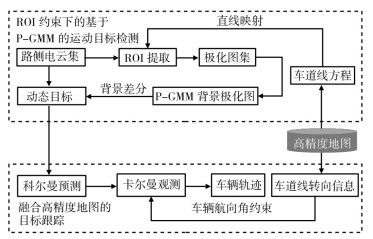
摘要: 在车路协同路侧感知研究中,由于点云数据量庞大且存在着不可避免的目标遮挡情况,导致检测效率低、目标轨迹不稳定和跟踪精度低的问题。针对上述问题,提出了1种融合高精度地图的多激光雷达路侧智能感知方法,通过融合高精度地图信息,提高感知结果的准确性和可靠性。该方法分为3个部分:①通过多激光雷达的标定结果,利用高精度地图完成三维点云区域中感兴趣区域的提取,从而有效减少待处理点云的数量,提升计算效率;②基于极化图高斯混合背景模型的背景建模方法,利用极化图完成运动目标快速检测,避免大规模激光点云的直接处理,有效提升检测效率;③利用车辆航向与车道线方向一致性约束,将高精度地图中的车道方向转化为卡尔曼滤波框架下的车辆状态线性约束,改善车辆检测与轨迹跟踪的性能。实验中,分别在仿真交叉路口与实车实验道路双T形路口对算法与模型进行测试验证。相比于其他方法,所提出的方法数据量减少了55%,目标检测准确率提高了12%,耗时减少了56%,目标跟踪的误差极值、误差均值以及均方根误差均有所降低。实验结果表明:所提的方法能有效融合高精度地图信息,在大范围道路场景下实现对道路运动目标的快速检测与稳定跟踪。Abstract: In the research of vehicle-road collaborative roadside perception, challenges such as low detection efficiency, unstable target trajectories, and inaccurate tracking arise due to the sheer volume of point cloud data and the inevitable obstruction of targets. To tackle these issues, a method of intelligent roadside perception utilizing multi-LiDAR fused with High-Definition (HD) maps is proposed. The goal is to enhance the accuracy and reliability of perception outcomes by incorporating detailed map information. Leveraging the calibration results of multi-LiDAR, the extraction of the region of interest (ROI) within the three-dimensional point cloud is achieved through HD maps, effectively reducing the quantity of point clouds for processing and enhancing computational efficiency. Employing the polar-image Gaussian mixture model (P-GMM) for background modeling, moving targets are swiftly identified using polar-images to circumvent direct processing of extensive LiDAR point clouds, thereby boosting detection efficiency. By enforcing the alignment between vehicle heading and lane line direction, the lane orientation in the HD map is translated into a linear constraint of vehicle state within the Kalman filter framework, thereby enhancing the efficacy of vehicle detection and trajectory tracking. Experimental validation is conducted using simulated crossroads and real-world roads with double T-shaped intersections. Compared to other methods, the method proposed yielded a 55% reduction in data volume, a 12% increase in target detection accuracy, and a 56% decrease in processing time. The improvements in extreme error, mean error, and root mean square error are also achieved in target tracking. The experimental results show that the method proposed can fuse HD map information effectively, achieving rapid detection and tracking of road-moving targets in a wide range of road scenarios.
-
Key words:
- intelligent transportation /
- roadside perception /
- target tracking /
- Kalman filter /
- High-Definition map /
- polar-image
-
表 1 基于仿真平台的目标检测算法对比
Table 1. Comparison of target detection algorithms based on simulation platform
数据帧 方法 目标数量 错误检测 准确率/% 耗时/ms 27 基于整个场景的目标检测 6 1 83.33 127 本文算法 0 100.00 53 331 基于整个场景的目标检测 16 3 81.25 158 本文算法 1 93.75 68 756 基于整个场景的目标检测 21 3 85.71 174 本文算法 1 95.24 79 合计 基于整个场景的目标检测 43 7 83.72 459 本文算法 2 95.35 200 表 2 仿真环境下不同算法车辆跟踪误差对比分析
Table 2. Comparative analysis of vehicle tracking errors in simulation environments
表 3 基于实车实验场景的目标检测算法对比
Table 3. Comparison of target detection algorithms based on real vehicle experiment scene
数据帧 方法 目标数量 错误检测 准确率/% 耗时/ms 12 基于整个场景的目标检测 3 1 66.67 94 本文算法 0 100.00 55 表 4 基于实车实验场景的车辆跟踪误差对比分析
Table 4. Comparative analysis of vehicle tracking errors based on real vehicle experiment scene
-
[1] 张亚勤, 李震宇, 尚国斌, 等. 面向自动驾驶的车路云一体化框架[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2023, 14(3): 249-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2023.03.001ZHANG Y Q, LI Z Y, SHANG G B, et al. A unified framework for vehicle-infrastructure-cloud autonomous driving[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy Saving, 2023, 14(3): 249-273. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2023.03.001 [2] 辜志强, 吉鑫钰, 褚端峰, 等. 基于全局位置精度损失最小化的路侧多传感器目标关联匹配方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(3): 286-294.GU Z Q, JI X Y, CHU D F, et al. A roadside multi-sensor target association matching method based on minimization of global position precision loss[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(3): 286-294. (in Chinese) [3] 任柯燕, 谷美颖, 袁正谦, 等. 自动驾驶3D目标检测研究综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(4): 865-889.REN K Y, GU M Y, YUAN Z Q, et al. 3D object detection algorithms in autonomous driving: a review[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(4): 865-889. (in Chinese) [4] BELTRAN J, GUNIDEL C, MORENO F M, et al. BirdNet: a 3D object detection framework from LiDAR information[C]. 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC). Maui, HI: IEEE, 2018. [5] 孙挺, 齐迎春, 耿国华. 基于帧间差分和背景差分的运动目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1325-1329.SUN T, QI Y C, GENG G H. Moving object detection algorithm based on frame difference and background subtraction[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(4): 1325-1329. (in Chinese) [6] ZHANG Z, ZHENG J, XU H, et al. Automatic background construction and object detection based on roadside LiDAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(10): 4086-4097. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2936498 [7] 李杰, 张洛维, 王晓燕, 等. 基于视锥距离和自适应权重卡尔曼滤波的多传感器融合算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2024, 37: 194-203.LI J, ZHANG L W, WANG X Y, et al. A multi-sensor fusion algorithm based on view-cone distance and adaptive weighted Kalman filter[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2024, 37: 194-203. (in Chinese) [8] 徐国艳, 牛欢, 郭宸阳, 等. 基于三维激光点云的目标识别与跟踪研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(1): 38-46.XU G Y, NIU H, GUO C Y, et al. Research on target recognition and tracking based on 3D laser point cloud[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(1): 38-46. (in Chinese) [9] ZHAO J, XU H, LIU H, et al. Detection and tracking of pedestrians and vehicles using roadside LiDAR sensors[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 100: 68-87. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2019.01.007 [10] LIN C, WANG Y, GONG B, et al. Vehicle detection and tracking using low-channel roadside LiDAR[J]. Measurement, 2023, 218: 113159. [11] YANG B, LIANG M, URTASUN R. HDNET: exploiting HD maps for 3D object detection[C]. 2nd Conference on Robot Learning, Zürich, Switzerland: PMLR, : 2018. [12] 杨振凯, 华一新, 訾璐, 等. 浅析高精度地图发展现状及关键技术[J]. 测绘通报, 2021(6): 54-60.YANG Z K, HUA Y X, ZI L, et al. Analysis of the development status and key technologies of high-precision map[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2021(6): 54-60. (in Chinese) [13] SEIF H G, HU X. Autonomous driving in the ICity—HD maps as a key challenge of the automotive industry[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(2): 159-162. [14] MA W C, URTASUN R, TARTAVULL I, et al. Exploiting sparse semantic HD maps for self-driving vehicle localization[C]. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS). Macau, China: IEEE, 2019. [15] CAI H, HU Z, HUANG G, et al. Integration of GPS, monocular vision, and high definition(HD)map for accurate vehicle localization[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3270. [16] GHALLABI F, NASHASHIBI F, EI-HAJ-SHHADE G, et al. LiDAR-based lane marking detection for vehicle positioning in an HD map[C]. 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC). Maui, HI: IEEE, 2018. [17] 胡钊政, 孙勋培, 张佳楠, 等. 基于时空图模型的车-路-图协同定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1246-1257.HU Z Z, SUN X P, ZHANG J N, et al. Vehicle-infrastructure-map cooperative localization method based on spatial-temporal graph model[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1246-1257. (in Chinese) [18] BAUER S, ALKHORSHID Y, WANIELIK G. Using high-definition maps for precise urban vehicle localization[C]. 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2016. [19] JIANG K, YAND D, LIU C, et al. A flexible multi-layer map model designed for lane-level route planning in autonomous vehicles[J]. Engineering, 2019, 5(2): 305-318. [20] 王丞, 田暄, 郭瑞, 等. 自适应Harris角点提取的点云粗配准算法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2022, 56(3): 33-44.WANG C, TIAN X, GUO R, et al. Coarse point cloud registration based on adaptive Harris corner extraction[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(3): 33-44. (in Chinese) [21] 叶雅欣, 王佳盛, 吴烽云, 等. 消毒机器人目标识别定位与包围盒优化[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(4): 346-354.YE Y X, WANG J S, WU F Y, et al. Target recognition and localization, bounding box optimization of disinfection robot[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(4): 346-354. (in Chinese) [22] 赵洲, 黄攀峰, 陈路. 1种融合卡尔曼滤波的改进时空上下文跟踪算法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(2): 274-284.ZHAO Z, HUANG P F, CHEN L. An improved spatiotemporal context tracking algorithm fused with Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Aeronautics, 2017, 38(2): 274-284. (in Chinese) [23] DOSOVITSKIY A, ROS G, CODEVILLA F, et al. CARLA: An open urban driving simulator[C]. The First Annual Conference on Robot. Machine Learning, Mountain View, California: PMLR, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: